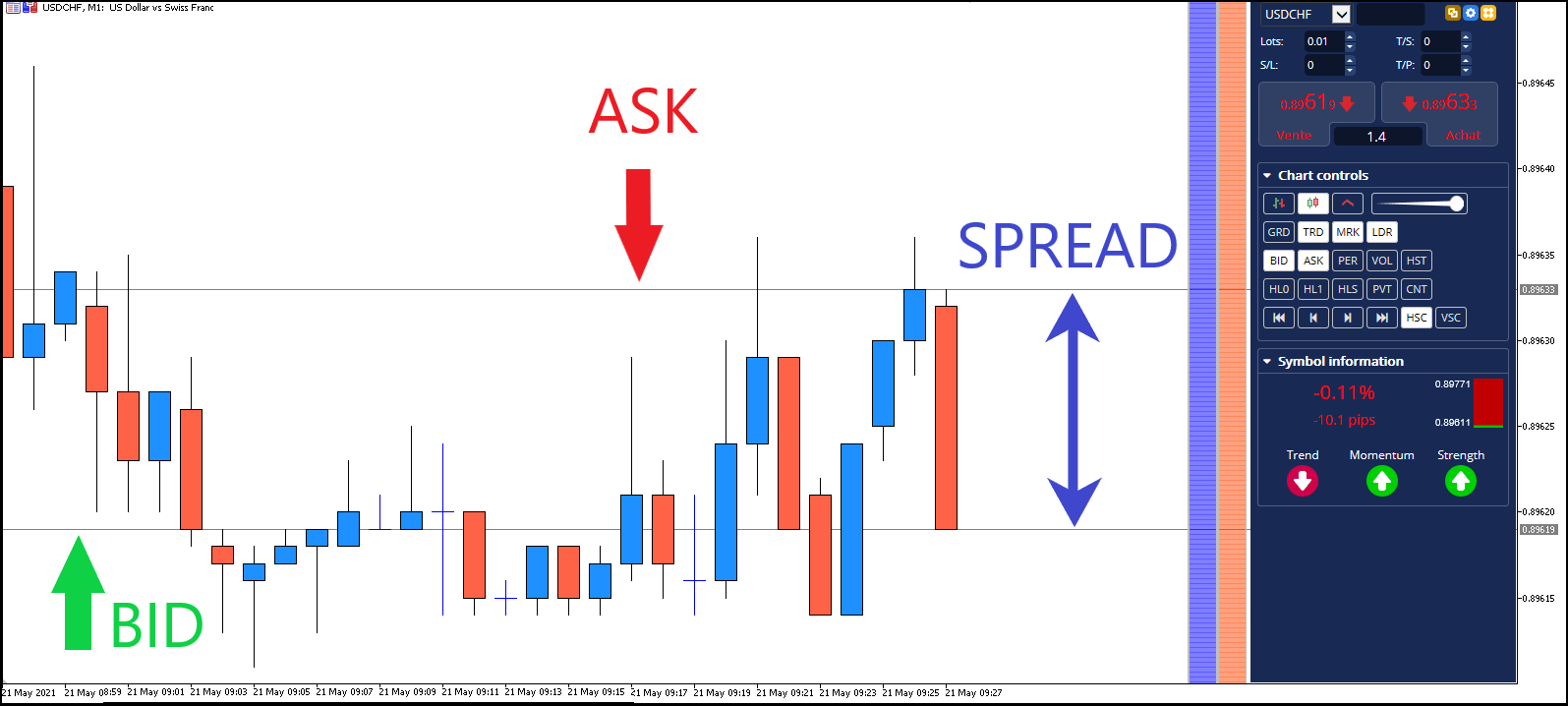
Spread in the crypto world refers to the difference between the ask price and the bid price of a cryptocurrency on an exchange. This difference represents the actual cost of executing a trade on a particular platform, and unlike a fee, which is usually a fixed amount or percentage specified by the exchange, the spread can change in real time depending on market conditions and liquidity.
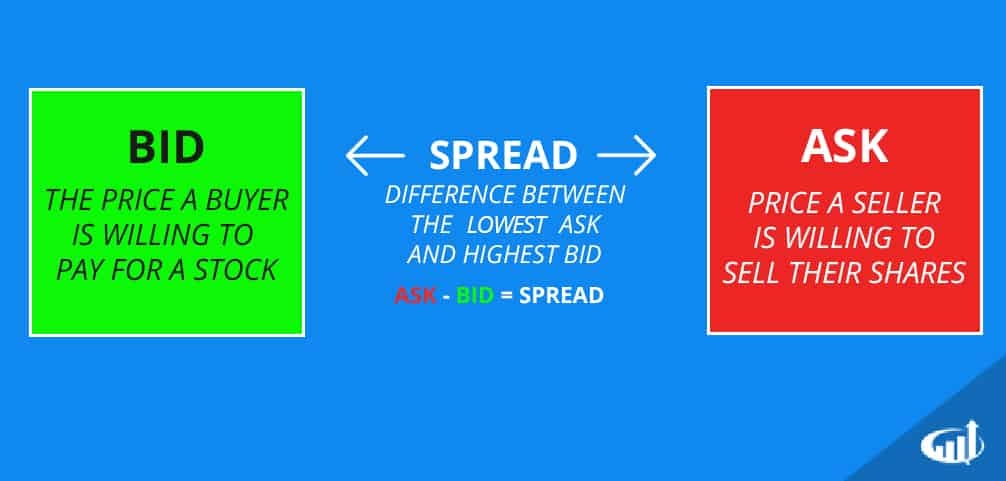
Unlike a commission, which is charged by an exchange to process a transaction, a spread is not a direct charge, but rather an implicit cost that traders pay when executing trades. The commission is often transparent and stated before trading, whereas the spread can vary and requires trader attention to minimize trading costs.
For example, if the purchase price of Bitcoin is $40,000 and the sale price is $39,950, the spread is $50. This difference is the actual cost of buying or selling the cryptocurrency, in addition to any fees that may be charged by the exchange. Therefore, the spread affects the profitability of trading, especially for high-volume or frequent trades.
Factors Affecting Spread
Spreads in the crypto world can vary significantly depending on several key factors:
- Market Liquidity : Liquidity refers to the ability of a market to allow assets to be bought or sold at stable, transparent prices. Higher liquidity usually means a smaller spread, as the difference between the bid and ask prices is reduced by a large number of buyers and sellers.
- Trading Volume : Closely related to liquidity, the trading volume on a particular exchange or within a particular cryptocurrency will also affect the spread. Exchanges with higher trading volumes often have tighter spreads, as high volume increases the likelihood of matching buy and sell orders being found instantly.
- Cryptocurrency Volatility : High volatility increases uncertainty about future prices, which can lead to widening spreads. Traders and market makers may increase the spread to compensate for the potential risk of rapid price changes.
- Order Type : Depending on whether a market order or a limit order is used, the spread may vary. Market orders, which are executed immediately at the current market price, are often subject to higher spreads, especially during times of low liquidity. Limit orders, which are executed only at a specified price or better, can help avoid buying or selling assets at unfavorable prices.

Understanding these factors can help traders choose exchanges and trading strategies that minimize spread costs and maximize potential profits.
The difference between the spread on the crypto exchange and the stock market
When comparing cryptocurrency exchanges to a traditional stock market, such as stock trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), spreads on the stock market are typically lower for most liquid stocks due to established market trading mechanisms and regulations. However, spreads can also widen significantly for less liquid stocks or during periods of high volatility.
These differences highlight the importance of understanding spreads and their impact on trading strategies. For day traders and those who engage in arbitrage, choosing a platform with low spreads is critical to minimizing trading costs and maximizing profitability.
Conversely, investors who are into long-term investing may be less sensitive to spreads, focusing more on the overall market trend and the stability of the chosen platform.

Examples of spreads on different exchanges
Spreads on popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple can vary significantly depending on the exchange you choose. On large platforms like Binance or Coinbase, spreads tend to be relatively low due to high liquidity and trading volumes. For example, spreads on Bitcoin can range from a few dollars to tens of cents. This makes these exchanges attractive to active traders who can conduct many transactions without incurring significant losses on spreads.
On the other hand, smaller platforms like Kraken or Bitstamp, although they offer competitive services, may have slightly higher spreads. This is due to less liquidity compared to the market giants. Spreads on these exchanges can reach several dollars, especially during periods of high volatility or when the market is experiencing rapid changes.
Smaller or specialized exchanges like Gemini or Luno, which may focus on specific regions or offer a more limited selection of currencies, will often have higher spreads. For example, the spread for Ethereum can be several times higher than on Binance, making them less favorable for large volume or short-term trading.
Therefore, traders need to consider not only the fees and the exchange interface, but also the spread sizes when choosing a platform to trade on. This is especially important for those who make a large number of transactions or work with large volumes of quotes, as even small differences in spreads can significantly affect the overall profitability of trading.
The impact of spread on trader’s profit

The spread has a significant impact on a trader’s profitability because it is one of the main variable costs associated with trading. Each trade starts with a small loss equal to the spread, meaning that the asset price must move sufficiently in the positive direction before the trader can break even or make a profit.
For example, if the bid/ask spread for Bitcoin is $50, a trader must wait for the price of Bitcoin to rise by at least $50 just to cover the cost of the spread. If the trader plans to close the position quickly, this price change must occur in a short time frame, which increases risk and jeopardizes potential profits, especially in low-volatility market conditions.
Moreover, in highly volatile order conditions, where prices change quickly and unexpectedly, spreads can widen, increasing the cost of the transaction and further reducing the trader’s profitability. This is especially noticeable in less liquid markets or for rare cryptocurrencies, where normal spreads can be significantly higher, and sharp market movements can lead to their further widening.
Managing and minimizing spreads is therefore a critical aspect of successful trading. Effective traders seek to trade on exchanges with low spreads and employ strategies that take into account possible changes in spreads under different market conditions.
It is also important to choose times to trade when spreads tend to be tighter, such as during periods of high market activity when liquidity increases.
Spreads for trading popular cryptocurrencies
To create a comparison table of spreads for popular cryptocurrencies on different exchanges, we need to take into account a number of factors, such as market volatility, the current time (as spreads can change depending on the time of day and market conditions), and the available data from each exchange.
Below is a simplified table that shows approximate spreads for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin ( BTC ), Ethereum (ETH) and Ripple (XRP) on several popular exchanges.
Spread table for popular cryptocurrencies
| Exchange | Bitcoin (BTC) | Ethereum (ETH) | Ripple (XRP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | $10 — $30 | $5 — $10 | $0.005 — $0.01 |
| Coinbase | $20 — $50 | $7 — $15 | $0.01 — $0.02 |
| Kraken | $15 — $35 | $6 — $12 | $0.004 — $0.008 |
| Bitfinex | $15 — $40 | $6 — $14 | $0.01 — $0.015 |
| KuCoin | $10 — $25 | $5 — $11 | $0.005 — $0.01 |
| Gemini | $18 — $45 | $7 — $16 | $0.01 — $0.02 |
Note : Spreads are shown as a range as they may fluctuate depending on current market conditions, time of day and specific exchange liquidity.
Table Analysis
- Exchanges with the lowest spreads : Binance and KuCoin often offer the lowest spreads for all three cryptocurrencies, making them the preferred platforms for traders interested in minimizing trading costs.
- Exchanges with the highest spreads : Coinbase and Gemini tend to have higher spreads, which may be due to their particularly strict regulatory standards and focus on security, which may increase their operating costs.
When choosing an exchange, you should consider not only the spreads but also other factors such as security, user-friendliness, customer service, and available deposit and withdrawal methods. It is also important to remember that some exchanges may offer additional discounts on fees when using their native tokens or for users with high trading volumes.
Tips for choosing an exchange with low spreads

When deciding on a cryptocurrency exchange with low spreads, it is important to conduct thorough research to determine the most favorable trading conditions. Here are some tips to help in this process:
Studying reviews about the exchange
The first step should be to read reviews from other users and analyze their experience with the exchange. Reviews often mention not only spreads, but also other aspects such as the quality of customer service, transaction processing speed, and problems that users have encountered. Resources such as forums, specialized websites, and social media can provide valuable information about the reputation and reliability of the exchange.
Taking other factors into account
- Commissions : In addition to spreads, it is important to consider other fees charged by the exchange, such as deposit, withdrawal, and trading fees. Some exchanges may offer low spreads but charge high fees for other transactions, which can reduce the overall profitability of trading.
- Liquidity : High liquidity is important for maintaining low spreads as it allows for high trading volumes, which in turn reduces the spread between bid and ask prices. Exchanges with a large number of active users and high trading volumes often offer more competitive spreads.
- Security : It is equally important to ensure that the exchange has robust security measures in place to protect user funds and data. Security should be a priority, as even low spreads will not compensate for the loss of funds due to hacker attacks.
Choosing an exchange with low spreads requires a comprehensive approach, including an assessment of all trading conditions and the overall reputation of the platform. Careful analysis and comparison of different platforms will help you find the most favorable trading conditions, balancing low spreads with other important factors such as fees, liquidity and security.
Conclusion
To conclude our discussion of the spread in trading, it is worth emphasizing its importance as a critical element in the structure of trading costs. The spread, as the difference between the purchase and sale price of an asset, directly affects the profitability of trading operations. In conditions of high liquidity, spreads are usually lower, making trading more economical, while in periods of low liquidity or high volatility, spreads can widen, increasing trading costs.

Answers to frequently asked questions
- What is a spread and why is it important? A spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of an asset. It is important because every trade starts with a small loss equal to the spread. A trader needs the asset price to move enough to cover the spread before they can make a profit.
- How to Minimize Spread Costs? To minimize spread costs, traders can choose exchanges with high liquidity and low spreads, trade during periods of high market activity when spreads tend to be tighter, and use limit orders, which allow control over maximum and minimum execution prices.
- How does the spread affect short-term and long-term trading? In short-term trading, where every pip counts, high spreads can significantly reduce profits or increase losses. For long-term investors who hold positions for many weeks, months, or even years, the impact of the spread is usually less significant, but should still be considered when entering or exiting positions.
Understanding and managing spreads are fundamental aspects of successful trading. Studying market conditions in advance and choosing the right strategy can help optimize trading operations and improve overall trading results.
Автор Evgeniy
IT предприниматель. Консультирую команду Buycrypt по организации децентрализованной экономики. Разрабатываю стратегию вывода на рынок ценностного предложения токена. Работаю над математическими моделями: - повышение эффективности торговли фонда методом коллективного принятия решений. - коэффициент интеллекта трейдера для расстановки весов влияния на коллективное решение. - расчет справедливости распределения доходов и вклада. - прогностический алгоритм на основе реакций масс. - система принятия решений и организация ввода/вывода активов.




