Cryptocurrency arbitrage is the online purchase of cryptocurrency in one trading pair and selling it in another to make a profit on the difference in rates. Intra-exchange arbitrage occurs on the same exchange but in different trading pairs using related cryptocurrencies. For example, exchanging Ethereum for Bitcoin , Bitcoin for USDT, and then USDT for Ethereum. Inter-exchange arbitrage, in turn, involves buying on one exchange and selling on another. This method requires a certain level of experience and consideration of factors such as spread, liquidity, and withdrawal speed.
Essentially, it is a process of making a profit from the difference in the price of the same cryptocurrency on different exchanges. Arbitrage traders buy cryptocurrency on an exchange where it is cheaper and sell it on an exchange where the price is higher. This allows them to profit from price imbalances.
How did cryptocurrency arbitrage come about?

The history of cryptocurrency arbitrage began to develop in the early stages of the market. At that time, the cryptocurrency market was characterized by low liquidity and a limited number of exchanges. Here are some key points related to the emergence of arbitrage in the world of cryptocurrency:
- The Birth of Cryptocurrency : In 2009, Bitcoin ( BTC ) was created, the first cryptocurrency based on blockchain technology . This event became the starting point for the development of the cryptocurrency market. As cryptocurrencies grew in popularity, more traders and investors began to participate in these markets, which increased trading volumes and increased arbitrage opportunities.
- High Volatility of Cryptocurrencies : Cryptocurrencies are known for their high volatility. Rapid price changes can create significant discrepancies between exchanges, making arbitrage particularly attractive.
- The rise of exchanges : With the emergence of new cryptocurrencies and the growing interest in them, new exchanges emerged. Each exchange had its own rates and spreads, which created opportunities for arbitrage. With the emergence of cryptocurrency exchanges around the world, differences in the quotes of the same cryptocurrency arose. These differences are due to differences in liquidity, trading volumes, trading rules, and exchange opening hours.
- Arbitrage opportunities : Arbitrageurs began to pay attention to the differences in prices of the same cryptocurrencies on different exchanges. They bought assets on the exchange with a lower price and sold them on the exchange with a higher price, making a profit on the difference.
- Technological advancement : With the advancement of technology and the advent of automated trading bots, arbitrage became more efficient. Bots could instantly react to price changes and execute trades without delay.
- Cross-exchange arbitrage : Arbitrageurs began using cross-exchange arbitrage by buying and selling cryptocurrencies across different exchanges. This required quickly transferring assets between exchanges and accounting for fees.
- Regulatory and economic factors : Different countries may have different regulations, taxes, and economic conditions, which affects the supply and demand of cryptocurrencies on local exchanges. These factors also contribute to price discrepancies.
- Technical and geographical differences : Exchanges may be located in different time zones and have different levels of technological infrastructure. This results in differences in the speed of quote updates and trade processing, which creates opportunities for arbitrage.
Today, cryptocurrency arbitrage continues to develop, and many traders use it as a tool for making money in the cryptocurrency market.
How Crypto Arbitrage Works
The basic idea of crypto arbitrage is to buy cryptocurrency on one exchange at a lower price and sell it on another exchange at a higher price.
Monitoring the value of cryptocurrency on exchanges
Traders constantly monitor prices on different exchanges to find differences in prices for the same cryptocurrency. These differences may arise due to differences in supply and demand, the speed of updating quotes, and other factors. During the monitoring process, trading pairs are identified in which the rate of the same cryptocurrency differs.
For example, if Bitcoin (BTC) is trading on Exchange A at $35,000 and on Exchange B at $35,200, a trader can buy BTC on Exchange A and sell it on Exchange B, earning the difference of $200.
Buying and selling
When a trader finds an opportunity, they buy cryptocurrency on an exchange with a lower price and simultaneously sell it on an exchange with a higher price. Sometimes this can happen almost instantly if traders use automated trading systems.
The profit from arbitrage should be sufficient to cover all transaction costs such as trading fees, withdrawals, transfers between exchanges and possible taxes.
Transferring assets from one exchange to another

In some cases, cryptocurrency must be transferred from one exchange to another to complete an arbitrage transaction. This can take time and involve additional risks associated with transaction delays and price changes.
Crypto arbitrage can be risky due to the volatility of cryptocurrency markets, delays in transferring funds, and technical issues on exchanges. Traders should be aware of these risks and have strategies in place to minimize them.
Types of crypto arbitrage
There are several types of arbitrage in the cryptocurrency market that allow you to earn on the difference in prices between different exchanges and trading pairs. Here are some of them:
Inter-exchange arbitrage
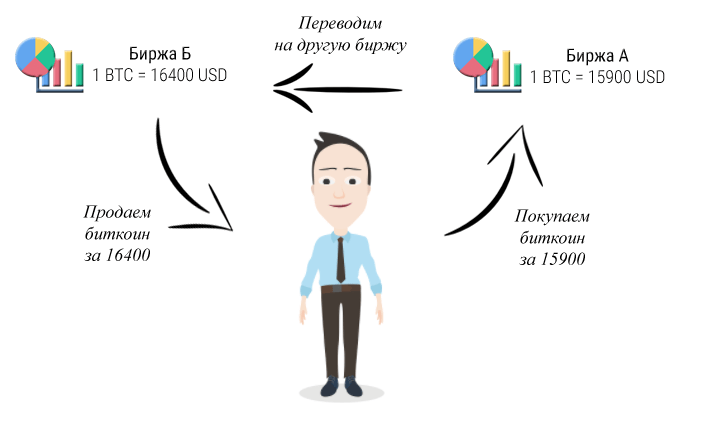
Inter-exchange arbitrage is a classic version of an arbitrage strategy in financial markets.
Inter-exchange arbitrage exploits the difference in prices of the same asset between different exchanges. Arbitrageurs try to make a profit by buying an asset on an exchange with a lower price and selling it on a platform where it is more expensive1.
Advantages of Inter-Exchange Arbitrage
- Arbitrage allows you to make a profit by using the difference in prices. The profit does not depend on the price movement, but on the difference between exchanges.
- Automated trading bots execute trades instantly, which is important for making a profit in rapidly changing cryptocurrency prices.
Risks of interexchange arbitrage
- Price differences can change quickly, which can impact profits.
- Some small exchanges have low liquidity, making it difficult to conduct transactions.
- Fast transactions are essential for successful arbitrage.
- Make sure that both exchanges support the deposit and withdrawal methods you need.
Example of inter-exchange arbitrage
Let’s say Ethereum is priced at $2,000 on one exchange (X) and $2,050 on another (Y). An arbitrageur could buy Ethereum on exchange X and sell it on exchange Y, making a profit from the difference in prices.
P2P arbitrage
P2P arbitrage is the process of buying and selling cryptocurrency on different exchanges in order to profit from the price difference. Instead of using classic centralized exchanges, P2P arbitrage uses platforms where transactions are carried out directly between users without intermediaries and identity verification.
For example, you buy Bitcoin on a centralized exchange (e.g. Binance ) at a low price and sell it at a premium on a P2P marketplace (e.g. Binance P2P) where users can exchange cryptocurrency directly with each other.
Advantages of P2P arbitrage

- Opportunity to earn money on price differences.
- Using P2P technology, bypassing intermediaries.
Risks of P2P arbitrage
- Price volatility.
- Delays in transactions.
- Possibility of deception by other participants.
P2P arbitrage requires an initial investment to purchase cryptocurrency. The larger the investment, the higher the potential profit.
You also need to consider transaction fees and tax obligations in your country.
Popular P2P Arbitrage Platforms
Some of the popular platforms include Bybit P2P, OKX P2P, Binance P2P, BingX P2P, MEXC P2P, and more.
Arbitrage using stablecoins
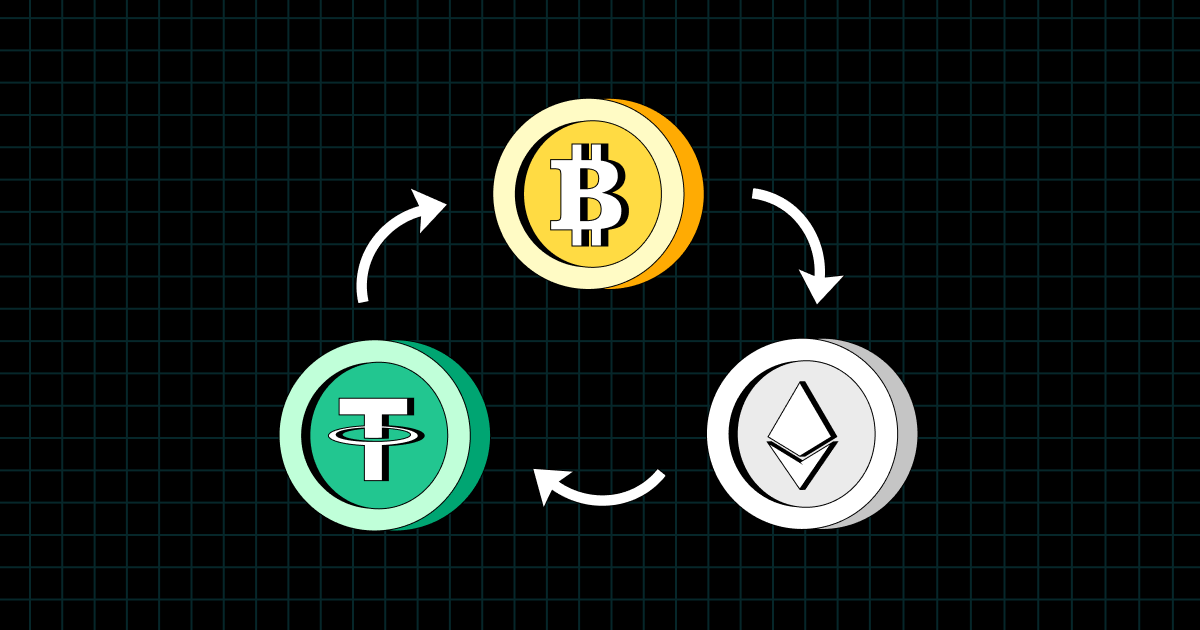
Stablecoin arbitrage is a trading strategy in which traders attempt to profit from price differences in the same asset across different markets or exchanges. Stablecoins such as USDT, USDC, and DAI provide stability because their value is pegged to fiat currencies, typically the US dollar.
Using stablecoins in arbitrage has several advantages, such as reducing volatility and simplifying calculations. Arbitrage and solutions using stablecoins can be divided into several types.
- Spatial arbitrage
- Triangular arbitrage
- Temporary arbitration
- Arbitrage on decentralized exchanges (DEX)
Spatial arbitrage
Spatial arbitrage involves buying an asset on one exchange where the price is lower and selling it on another exchange where the price is higher.
Process :
- Find a stablecoin (e.g. USDT) that is trading at different prices on two different exchanges.
- Buy stablecoin on an exchange with a lower price.
- Transfer the stablecoin to an exchange with a higher price.
- Sell the stablecoin on an exchange with a higher price and lock in the profit.
Advantages :
- A relatively simple strategy.
- Fast transactions thanks to the stable value of stablecoins.
Flaws :
- Transaction fees for transfers between exchanges.
- Delays in transfers may result in price changes and reduced profits.
Triangular arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage involves using the traffic of three different currencies to create a chain of transactions that returns you to the original currency at a profit.
Process :
- Start with a base currency (eg BTC).
- Exchange BTC for a stablecoin (eg USDT).
- Exchange USDT for another cryptocurrency (eg ETH).
- Exchange ETH back to BTC, locking in the difference in rate.
Advantages :
- Possibility of implementation within one exchange, which reduces transaction costs.
- Potentially high profits with low risks.
Flaws :
- Requires fast execution of trades to minimize the risk of price changes.
- Complexity and necessity of using automated systems for market monitoring.
Temporary arbitration
Time arbitrage is based on the difference in the execution time of trades in different markets. Trading with this strategy requires forecasting price changes.
Process :
- Analyze the market to identify regular patterns of price changes.
- Buy stablecoins when you expect demand to increase.
- Sell stablecoins when the price goes up.
Advantages :
- Using temporary market fluctuations to make a profit.
- Possibility of forecasting based on historical data.
Flaws :
- High level of uncertainty and risk.
- Deep market analysis and experience required.
Arbitrage on decentralized exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchange arbitrage involves using decentralized platforms such as Uniswap or SushiSwap to perform arbitrage operations.
Process :
- Find a stablecoin that is trading at different prices on DEX and CEX (centralized exchange).
- Conduct arbitrage trades between DEX and CEX to make profit.
Advantages :
- There is no need to go through the KYC process.
- The ability to quickly execute transactions thanks to smart contracts.
Flaws :
- High gas fees (especially on the Ethereum network).
- Risks associated with the use of smart contracts.
Monetary arbitrage
Monetary arbitrage is a trading strategy based on exploiting the difference in prices of the same financial instrument in different markets. The goal of monetary arbitrage is to buy an asset at a lower price in one market and sell it at a higher price in another, making a profit. In the context of cryptocurrency and stablecoins, this means exploiting the difference in prices of money and crypto assets between different exchanges or platforms.
Types of monetary arbitrage
- Currency arbitrage: the simplest type, uses the difference in exchange rates.
- Interest rate arbitrage: uses the difference in interest rates on loans and deposits.
- Securities arbitrage: exploits differences in the prices of securities in different markets.
An example of monetary arbitrage using stablecoins
- Identifying price differences :
- Let’s assume that on exchange A, the USDT stablecoin is trading at a price of 1.00 USD.
- At the same time, USDT is trading at 1.01 USD on Exchange B.
- Conducting an arbitration transaction :
- Buy 10,000 USDT on Exchange A for 10,000 USD.
- Transfer this 10,000 USDT to exchange B.
- Sell 10,000 USDT on Exchange B for 10,100 USD.
- Profit taking :
- You will earn 100 USD (10,100 USD – 10,000 USD), minus transaction and transfer fees.
Advantages of Monetary Arbitrage
- Minimizing Risk : Stablecoins have low volatility compared to other cryptocurrencies, which reduces the risk of loss.
- Simplicity : The basic idea is to buy low and sell high, which is relatively easy to understand and execute.
- Speed : Arbitrage trades can be executed quickly, especially when using automated systems.
Disadvantages of monetary arbitrage
- Transaction Costs : Fees for transfers between exchanges and for executing trades can reduce profits.
- Transfer Delays : The time it takes to transfer funds between exchanges can cause prices to fluctuate and reduce potential profits.
- Regulatory risks : Some countries and jurisdictions may impose restrictions on arbitrage operations or trading in cryptocurrencies.
- Competition : High competition among arbitrage traders can quickly eliminate price discrepancies.
Crypto Arbitrage Risk Analysis: Legality and Legal Nuances

Analyzing the risks of crypto arbitrage requires considering several aspects, including legality and legal nuances, which can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction. Let’s look at the main risks and legal aspects associated with crypto arbitrage.
The legality of crypto arbitrage depends on the specific laws and regulations in each country. In most jurisdictions, crypto arbitrage itself is not illegal, but compliance with local laws on cryptocurrencies and financial transactions is mandatory.
In the US, cryptocurrency trading is regulated by agencies such as the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and the CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission). Crypto arbitrage may require registration and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
In the European Union, cryptocurrencies are regulated by various directives such as AMLD5, which require crypto exchanges and financial institutions to perform AML and KYC procedures.

Regulation and licensing
Many jurisdictions require cryptocurrency trading platforms and apps to be licensed, including arbitrage firms.
Risks
- Lack of License: Conducting arbitration activities without a proper license may result in fines or business closure.
- Offshore registration: Offshore company registration may offer more lenient regulations, but also carries risks associated with possible non-recognition of these jurisdictions by other countries and difficulties in legal protection.
Tax liabilities
Income from crypto arbitrage may be subject to taxation. Different countries around the world have their own tax regimes for cryptocurrency transactions.
Risks
- Tax Failure: Failure to report crypto arbitrage income can result in severe tax penalties.
- Tax Law Changes: Unstable tax laws regarding cryptocurrencies may create uncertainty for arbitrage operations.
Risks associated with AML and KYC
Compliance with AML and KYC requirements is necessary to prevent cryptocurrencies from being used for illegal purposes.
Risks
- AML/KYC Failure: Failure to comply with these requirements may result in legal consequences, including fines and criminal prosecution.
- Privacy: KYC procedures can raise privacy concerns for users, which is important to consider when running an arbitrage platform.
Legal protection and dispute resolution
Due to the decentralized and international nature of cryptocurrencies, dispute resolution and enforcement can be complex.
Risks

- Jurisdictional conflicts: Difficulties in determining jurisdiction for dispute resolution, especially if transactions are conducted in different countries.
- Legal Protection: Lack of clear legal protection for crypto assets in some countries.
Compliance and internal policy
Companies that own assets and engage in crypto arbitrage must develop and implement internal policies to comply with the law and minimize risks.
Risks
- Lack of Internal Controls: Lack of adequate internal procedures can lead to errors and legal problems.
- Legislative Updates: Companies must continually monitor changes in legislation and adjust their procedures.
Crypto arbitrage requires careful consideration of legal and regulatory aspects. Both the company and the individual trader must monitor changes in cryptocurrency regulation. They must understand and comply with local laws and international standards, and, if necessary, consult with legal and tax specialists to minimize risks and ensure the legality of their operations.
How to Start Cryptocurrency Arbitrage. Tips and Advice
Getting started with crypto arbitrage requires careful preparation and understanding of many aspects of the process. Here is a step-by-step plan with tips and tricks for a successful start:
1. Study the basics and size of the market
- Understanding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies.
- Learn the basic principles of arbitrage, including the concept of price differences across different exchanges.
2. Market analysis
- Learn how different cryptocurrency exchanges work.
- Analyze historical price and trading volume data.
3. Registration on several exchanges
- Choose reliable exchanges with high trading volume and a good reputation.
- Make sure that the exchanges offer the cryptocurrency pairs you plan to use for arbitrage.
4. Selecting tools for monitoring and analysis
- Use specialized tools and services to track prices and trading volumes on various exchanges (for example, CoinMarketCap, CryptoCompare).
- Consider using bots and automated systems for more efficient arbitrage.
5. Determining the amount of initial capital
- Determine the amount you are willing to invest in arbitrage. Be aware of the risks and do not invest more than you can afford to lose.
6. Legal training
- Please check your country’s laws regarding cryptocurrencies and arbitration.
- Complete KYC and AML procedures on selected exchanges.
7. Opening accounts
- Register and verify on the selected exchanges.
- Top up your accounts on these exchanges with the required amounts in fiat money or cryptocurrency.
8. Developing a strategy
- Define the criteria by which you will look for arbitrage opportunities (e.g. minimum percentage of price difference).
- Plan the frequency of transactions and the cryptocurrency pairs used.
9. Trial operations
- Start with small trades to test your strategy and make sure the system works.
- Analyze the results and adjust your strategy as needed.
10. Diversification
- Don’t focus on one cryptocurrency or one exchange. Use multiple exchanges and different cryptocurrency pairs to reduce risks.
11. Volatility control
- Keep in mind that cryptocurrency prices can change dramatically. Use stop losses and other tools to minimize losses.
12. Process automation
- Consider using arbitrage bots to automate your trading. Popular tools include HaasOnline, Gekko, and others.
13. Security
- Keep your funds and data safe. Use two-factor authentication (2FA), cold wallets for storing your main assets, and strong passwords.
14. Market monitoring
- Constantly monitor changes in the market and analyze new arbitrage opportunities.
- Participate in cryptocurrency and arbitrage forums and communities to stay up to date with the latest trends and news.
15. Learning and improvement
- Learn new tools and strategies.
- Participate in online courses and webinars to improve your knowledge and skills.
Cryptocurrency arbitrage can be profitable, but it requires a careful approach and constant monitoring. By following these steps and recommendations, you can minimize risks and increase your chances of success in this area.
Автор Alex Smith
Has professional training in microelectronics and hardware programming, as well as over 30 years of experience working with data processing and transmission systems, including cryptocurrency mining equipment. When preparing materials for blog readers, BuyCrypt successfully applies its extensive technical background to convey the meaning of materials from the sources used as accurately as possible.
